WiFi
Overview
Raspberry Pi Version 4 supports a built-in Wifi adapter. The integrated antenna and low transmit power limits the throughput and communication range.
Adding an external USB-Wifi adapter overcomes some of these issues (eg.: using a high gain or directional antenna with the external adapter).
Most external USB-Wifi adapters do not work out of the box when plugged into the RPi. So we must identify the chip-set of the adapter, find the missing drivers and try to install them. An example how to install drivers for a specific USW-Wifi adapter is described in a separate document. Here I assume that we plugged an external Wifi adapter into some USB port of the RPi.
Setup
Figure 1‑1 shows what kind of wireless communication between a PC (Windows or Linux) and the Raspberry Pi (RPi) I would like to implement.
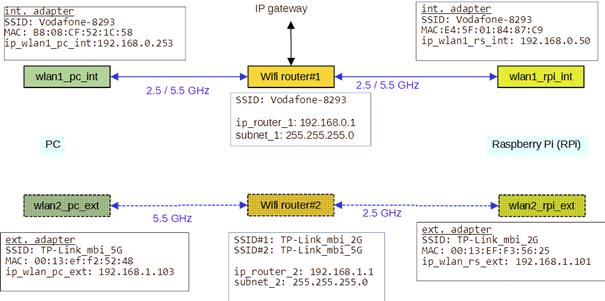
Two Wifi routers Wifi-router#1 and Wifi-router#2 shall enable the communication between PC and RPi. The characteristics of these routers are summarised in table 1‑1 and table 1‑2.
The PC has an internal Wifi adapter wlan1_pc_int and an external Wifi adapter wlan2_pc_ext. Similarly the RPi has an internal Wifi adapter wlan1_rpi_int and an external USB Wifi adapter wlan1_rpi_ext.
Wifi routers
Wifi-router#1 purpose: establish a bi-directional communication path between the internal Wifi-adapter of the PC and the internal Wifi-adapter of RPi
| property | description |
login name | some login name |
login password | some password |
SSID | Vodafone-8293 (SSID is common to frequency bands 2.5 / 5 GHz) |
keyword | <key_router_1> (user defined keyword) |
ip_router_1 | 192.168.0.1 / 24 |
DHCP | the DHCP server of the router is configured for some static IP4 addresses. MAC address IP address B8:08:CF:52:1C:58 192.168.0.253 D8:F2:CA:1D:5B:82 192.168.0.38 E4:5F:01:84:87:C9 192.168.0.50 |
Wifi-router#2 purpose: establish a bi-directional communication path between the external Wifi-adapter of the PC and the external Wifi-adapter of RPi
| property | description |
login name | some login name |
login password | some password |
SSID#1 | TP-Link_mbi_2G (SSID for frequency band 2.5 GHz) |
keyword (SSID#1) | <key_router_2_2ghz> (user defined key for 2 GHz communication) |
SSID#2 | TP-Link_mbi_5G (SSID for frequency band 5 GHz) |
keyword (SSID#2) | <key_router_2_5ghz> (user defined key for 5 GHz communication) |
ip_router_2 | 192.168.1.1 / 24 |
DHCP | the DHCP server of the router is configured for some static IP4 addresses. MAC address IP address 00:13:ef:f2:52:48 192.168.1.103 D8:F2:CA:1D:5B:82 192.168.1.102 00:13:EF:F3:56:25 192.168.1.101 |
Note:
Wifi router#1 and Wifi router#2 have IP-addresses on different subnets.
Wifi Adapters
As has been outlined before PC and RPi each use one internal and one external Wifi-adapter. Refer to Table 1‑3, Table 1‑4, Table 1‑5 and Table 1‑6 for the properties of these internal / external adapters.
PC / internal Wifi adapter
| property | description |
SSID | Vodafone-8293 |
MAC address | B8:08:CF:52:1C:58 (may be queried with ipconfig /all on PC (Windows) or ifconfig on PC (Linux) |
ip_wlan1_pc_int | IP address statically assigned by DHCP server of Wifi router#1 |
frequency band | either 2.5 or 5 GHz depending on what Wifi router#1 assigns to this interface |
PC / external Wifi adapter adapter: Realtek 8812BU Wireless LAN 802.11ac USB NIC
| property | description |
SSID | TP-Link_mbi_5G |
MAC address | B8:08:CF:52:1C:58 (may be queried with ipconfig /all on PC (Windows) or ifconfig on PC (Linux) |
ip_wlan2_pc_ext | IP address statically assigned by DHCP server of Wifi router#2 |
frequency band | 5 GHz |
Raspberry Pi / internal Wifi adapter
| property | description |
SSID | Vodafone-8293 |
MAC address | 00:13:EF:F3:56:25 may be queried with ifconfig on RPi |
| IP address statically assigned by DHCP server of Wifi router#1 |
frequency band | either 2.5 or 5 GHz depending on what Wifi router#1 assigns to this interface |
Raspberry Pi / external Wifi adapter adapter: Realtek 8812BU Wireless LAN 802.11ac USB NIC
| property | description |
SSID | TP-Link_mbi_2G |
MAC address | 00:13:EF:F3:56:25 may be queried with ifconfig on RPi |
ip_wlan2_pc_ext | IP address statically assigned by DHCP server of Wifi router#2 |
frequency band | 2.5 GHz |
Setting WPA_supplicant
The settings of the internal / external Wifi adapter of the Raspberry Pi must be configured via wpa_supplicant configuration files.
I found this link extremely helpful:
https://www.jeffgeerling.com/blog/2021/working-multiple-wifi-interfaces-on-raspberry-pi
The configuration files are in /etc/wpa_supplicant. The two wlan interfaces of the RPi are wlan0 and wlan1. For these interfaces two files namely
wpa_supplicant-wlan0.confwpa_supplicant-wlan1.conf
are created in directory /etc/wpa_supplicant. A directory listing is shown below:
The content this directory is shown here:
mbi1955@raspberrypi:~ $ cd /etc/wpa_supplicant/
mbi1955@raspberrypi:/etc/wpa_supplicant $ ls -al
total 68
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Feb 24 20:21 .
drwxr-xr-x 126 root root 12288 Feb 20 13:38 ..
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 937 Feb 25 2021 action_wpa.sh
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 25569 Feb 25 2021 functions.sh
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4696 Feb 25 2021 ifupdown.sh
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 154 Sep 22 05:19 wpa_supplicant.conf
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 155 Feb 24 20:21 wpa_supplicant-wlan0.conf
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 236 Feb 24 20:21 wpa_supplicant-wlan1.confAnd here is the content of the config files:
wpa_supplicant-wlan0.conf ; config file for interface wlan0
ctrl_interface=DIR=/var/run/wpa_supplicant GROUP=netdev
update_config=1
country=DE
network={
ssid="Vodafone-8293"
psk="WN_IR_2005"
key_mgmt=WPA-PSK
}wpa_supplicant-wlan1.conf ; config file for interface wlan1
ctrl_interface=DIR=/var/run/wpa_supplicant GROUP=netdev
ap_scan=2
update_config=1
country=DE
network={
ssid="TP-Link_mbi_2G"
psk="WN_IR_2005"
key_mgmt=WPA-PSK
}The configurations come into effect after rebooting the RPi (routers are already running). The result of this configuration can be inspected with command ip a.
The relevant entries are wlan0 (internal Wifi) and wlan1 (external Wifi). Obviously Routers 1/2 have successfully assigned the IP-addresses:
mbi1955@raspberrypi:~ $ ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: eth0: <NO-CARRIER,BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state DOWN group default qlen 1000
link/ether e4:5f:01:84:87:c8 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
3: wlan0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether e4:5f:01:84:87:c9 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.0.50/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute wlan0
valid_lft 604768sec preferred_lft 529168sec
inet6 2a02:8070:2986:dae0::cd54/128 scope global dynamic noprefixroute
valid_lft 43164sec preferred_lft 43164sec
inet6 fe80::173:bc62:ac38:6a0c/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
4: wlan1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:13:ef:f3:56:25 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.1.101/24 brd 192.168.1.255 scope global noprefixroute wlan1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::e537:bd38:885c:98d1/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft foreverUsing the ping command it is demonstrated that communication between PC – RPi is possible via both Wifi adapters.
PC to RPi via router#1:
ping -n 1 192.168.0.50
Ping wird ausgeführt für 192.168.0.50 mit 32 Bytes Daten:
Antwort von 192.168.0.50: Bytes=32 Zeit=56ms TTL=64
Ping-Statistik für 192.168.0.50:
Pakete: Gesendet = 1, Empfangen = 1, Verloren = 0
(0% Verlust),
Ca. Zeitangaben in Millisek.:
Minimum = 56ms, Maximum = 56ms, Mittelwert = 56msPC to RPi via router#2:
ping -n 1 192.168.1.101
Ping wird ausgeführt für 192.168.1.101 mit 32 Bytes Daten:
Antwort von 192.168.1.101: Bytes=32 Zeit=7ms TTL=64
Ping-Statistik für 192.168.1.101:
Pakete: Gesendet = 1, Empfangen = 1, Verloren = 0
(0% Verlust),
Ca. Zeitangaben in Millisek.:
Minimum = 7ms, Maximum = 7ms, Mittelwert = 7msRPi to PC via router#1:
ping 192.168.0.253
PING 192.168.0.253 (192.168.0.253) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.0.253: icmp_seq=1 ttl=128 time=5.52 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.0.253: icmp_seq=2 ttl=128 time=112 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.0.253: icmp_seq=3 ttl=128 time=130 msRPi to PC via router#2:
ping 192.168.1.103
PING 192.168.1.103 (192.168.1.103) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.1.103: icmp_seq=1 ttl=128 time=2.89 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.1.103: icmp_seq=2 ttl=128 time=3.30 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.1.103: icmp_seq=3 ttl=128 time=3.47 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.1.103: icmp_seq=4 ttl=128 time=3.40 msOther useful information can be obtained with command iwconfig:
mbi1955@raspberrypi:~ $ iwconfig
lo no wireless extensions.
eth0 no wireless extensions.
wlan0 IEEE 802.11 ESSID:"Vodafone-8293"
Mode:Managed Frequency:5.5 GHz Access Point: 94:8F:CF:8F:44:99
Bit Rate=292.5 Mb/s Tx-Power=31 dBm
Retry short limit:7 RTS thr:off Fragment thr:off
Power Management:on
Link Quality=51/70 Signal level=-59 dBm
Rx invalid nwid:0 Rx invalid crypt:0 Rx invalid frag:0
Tx excessive retries:10 Invalid misc:0 Missed beacon:0
wlan1 IEEE 802.11bgn ESSID:"TP-Link_mbi_2G" Nickname:"<WIFI@REALTEK>"
Mode:Managed Frequency:2.422 GHz Access Point: 6C:5A:B0:F2:7B:30
Bit Rate:300 Mb/s Sensitivity:0/0
Retry:off RTS thr:off Fragment thr:off
Power Management:off
Link Quality=100/100 Signal level=-49 dBm Noise level=0 dBm
Rx invalid nwid:0 Rx invalid crypt:0 Rx invalid frag:0
Tx excessive retries:0 Invalid misc:0 Missed beacon:0Resources
https://www.jeffgeerling.com/blog/2021/working-multiple-wifi-interfaces-on-raspberry-pi
